COLORS AND PIEBALDS
ONLINE TRANSLATED *WILL BE UPDATED SOON
Topics of this subpage:
- Color variations with pictures
- Color comparisons with pictures
The original coat pattern of a degus is agouti (wild-colored), meanwhile there are also blue- / blue agouti (anthracite-gray to steel blue), sand- / red (clay-colored to cream), cream (light red- / sand-colored with gray) and black as well as on top based color deviations such as chocolate, blue non agouti, lilac. In addition, various piebalds ranging from blessen, point piebald, strong piebald up to super piebald.
Many color variants are caused by a recessive gene, which means, as with many other animal species, that degus with
these colors come from a history of inbreeding. In the meantime, the color variants are stable again thanks to the crossing of healthy basic
colors.
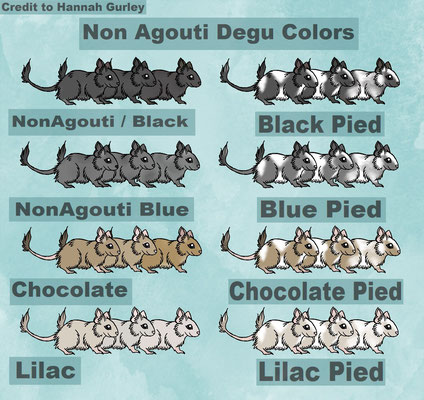
COLOURS
Below is a graphic representation of the current colors at Degus with English color names.
graphic copyright to Hannah Gurley (Dezi Pheonix) - Thank you!
Agouti (natural colour)
Name: Agouti, natural colour, red-brown
Genotype: (AA or Aa ) Gene code: A / - D / - E / - w / w
Mutation: Dominant
The fur shows what is known as "ticking". Ticking means that every hair has a band of at least two colors. In agouti, these are reddish-yellow and black, which makes the hair appear brown-black; the belly is lighter in color. The eyes are black. The wild color agouti is inherited dominantly, the hair is brown in the middle and gray / black-brown at the tip and in the undercoat. The fur around the eyes, ears, stomach and neck is noticeably lighter. The agoutilocus (a) is the gene for the agouti signaling peptide (ASIP), whose function is simultaneously influenced by the melanocortin receptor 1 (MC1R), which is encoded by the extension locus (E).
Blau-/ Blue Agouti (ANTHRACITE GRAY TO STEEL BLUE)
Name: Blue Agouti, blue, silver, gray
Genotype: (d / d) Gencode: A / - d / d E / - w / w
Mutation: dilution, recessive
Blue, the second color variant that was bred, is inherited recessively and causes a lightening of the entire coat in a homozygous manner. This is probably due to a mutation in the color of the agoutis that separated the brown and gray part of the coat color. Here, too, the color of the fur around the eyes, ears, stomach and neck is significantly lighter. If you look at the blue variants in other animal species, it can be assumed that they all have the same mutation called dilution (d / d).
In different animal species, different genes are referred to as the dilute gene, the mutations of which lead to a lightening of the intensity of the coat color.
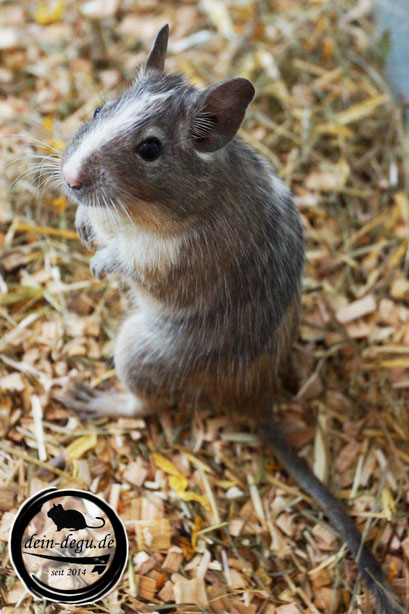
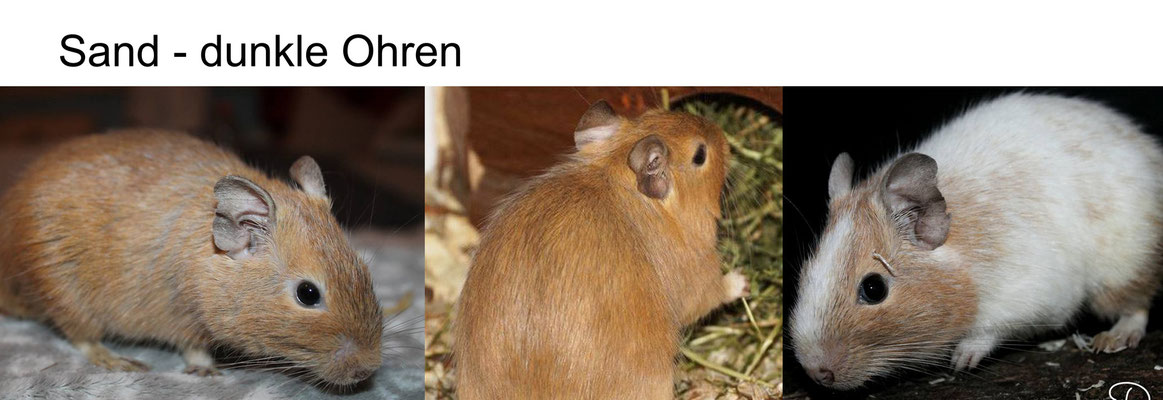
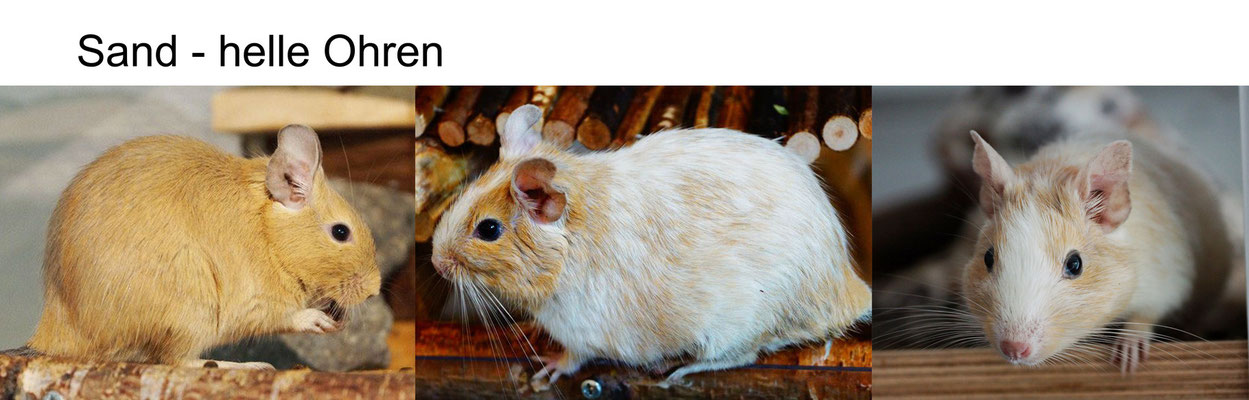
SAND / RED (CLAY COLORS TO SAND YELLOW)
Name: sand, red, beige, yellow, recessive red
Genotype: (e / e ) Gencode: A / - D / - e / ew / w
Mutation: extension, recessive
Sand-colored degus have been around for a number of years, the color is inherited recessively. The lightening of the coat color around the eyes, ears, stomach and neck is only faintly visible here. The extension mutation is recessive and homozygous causes the red pheomelanin to spread throughout the hair, so that dark eumelanin is no longer visible.
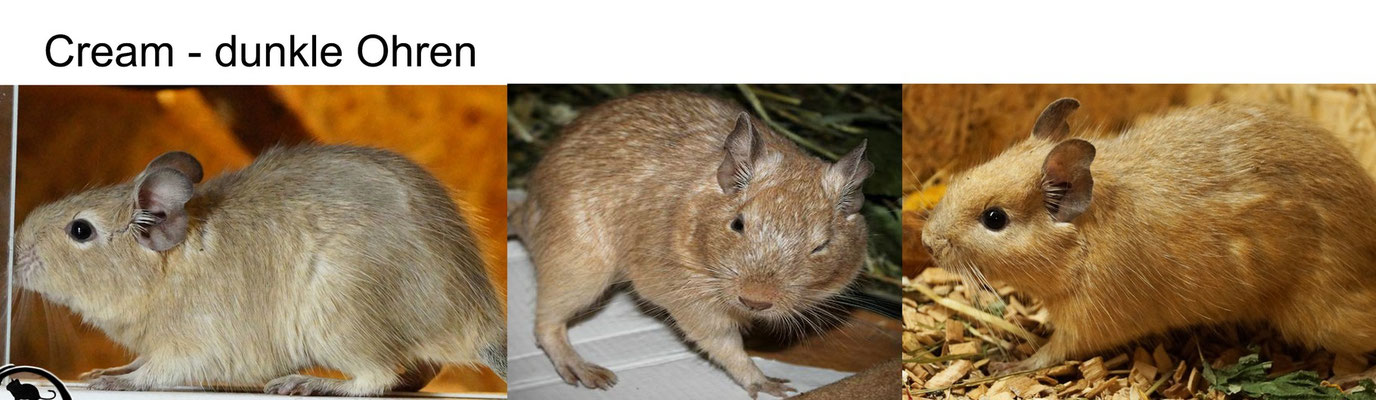
Cream (LIGHT RED / SAND TONE WITH GRAY)
Name: Champagne, Dove Agouti
Gene code: A / - d / de / ew / w
Mutation: recessive
Cream / Crème Degus has only been around for a short time, it was created through the pairing of sand-colored and blue animals. The fur is lighter than that of sand-colored (red) degus, the color is reminiscent of champagne. When the degus are fully grown, the coat color changes and becomes darker, the tips of the hair turn gray.
Black (Non Agouti)
Genotype: (a / a ) Gencode: a / a D / - E / - w / w
Mutation: non-agouti, recessive
The mutation causes the black eumelanin to spread throughout the hair from root to tip, while the yellow pheomelanin is no longer visible. Thus, non-agouti has exactly the opposite effect to the red lightening (sand). Mutations in the agouti locus can enlarge the black areas in the coat pattern ( nigrism ) until, in extreme cases, the entire body is black ( scotasmus ), so "melanism" arises to varying degrees. Melanism caused by the agoutilocus is inherited recessively.
Black degus that have other colors (e.g. sand) can often be slightly discolored. Rust-colored spots often show an indication of the recessive color carrier property.
CHOCOLATE
Name: chocolate, cinnamon, brown
Gene code: a / ab / b D / - E / ew / w
Mutation: non-agouti, recessive
Real chocolate is a non-agouti and is caused by the (b - brown) gene. This dilutes the black pigment in the fur to a dark brown (with color variations). It's a simple recessive gene, so it must be inherited from both parents. As young animals, the real chocolate color is very pronounced.
BLUE Non-AGOUTI (BNA)
Name: Blue Non-Agouti, Slate Blue
Gene code: a / a B / - d / d E / - w / w
Mutation: non-agouti, recessive
Also known as BNA or Slate Blue. A non-agouti mutation due to the dilution with the blue gene. The diluted gene results in many different shades of blue, from very pale with a white primer to deep slate (British blue). The different shades of blue are not a new color, just a color variation. The different shades are usually due to modifiers, not different genes, in the future the different shades will be given new names.
Lilac
Name: Lilac
Gene code: a / a B / - d / de / ew / w
Mutation: non-agouti, recessive
Lilac is a non-agouti mutation with two copies of the chocolate gene and two copies of the blue gene Phenotype: Chocolate-Dilution, Blue Non Agouti-Dilution. The color should be exactly between blue and chocolate, a shimmering, even gray-silver, never matt or blue / brownish discoloration.
White
Name: White, High White
Mutation: Dominant
The white color is not an albino mutation, but a breeding result of the dilution of the sand-colored extension with the blue dilution.
TRICOLOR BLUE AND AGOUTI / CHOCOLATE / SAND / CREAM WITH WHITE DRAWING
Strictly speaking, white is not a color, but I still present this color as tricolor / three-colored / multi-colored. So far nothing is known about the inheritance of this coloring, all three-colored degus are random litters.
The first three pictures are blue corners with sand / brown mahogany shimmers.
The latter picture is a blue checkin with sand-colored dot from Littlekings Degus.
The pictures below show a Blue Starkscheckin ST (Tricolore) whose entire fur has a strong brown tone. It comes from its own offspring and is not related to the Tricolore shown above.
COLOR CHANGE OF THE TWO TRICOLORE BROTHERS
Patched / Piebalds / Spotting
Spots, heterozygous (w / w), (agouti / - blue / - sand with white) now often appear with the three "basic colors" of degus, but there are also spotted between other colors or three-colored degus blue / sand / white, Strictly speaking, white is not considered a color. The spotting is inherited dominantly.
Pure-bred piebalds W / W (homozygous) "Whitelings" are very rare when two piebalds are mated. Whitelings have no pigmentation in their fur, not even around the eyes, neck or tail as is the case with super piebalds. Whites do not have a long life expectancy or usually die after a short time. Please do not confuse it with super piebalds!
Degus are given different names depending on the proportion of white; Pinto, strong pinto or super piebald. In animals with a very high proportion of white, areas of hair with residual color can often only be seen around the eyes, ears and on the tail.
Schecke (dot piebald / blaze) as soon as the white portion can be seen
Starkschecke approx. 40-70% white
Superschecke approx. 80% or more white
The colors change slightly depending on the lighting mood.
AGOUTI PIEBALDS
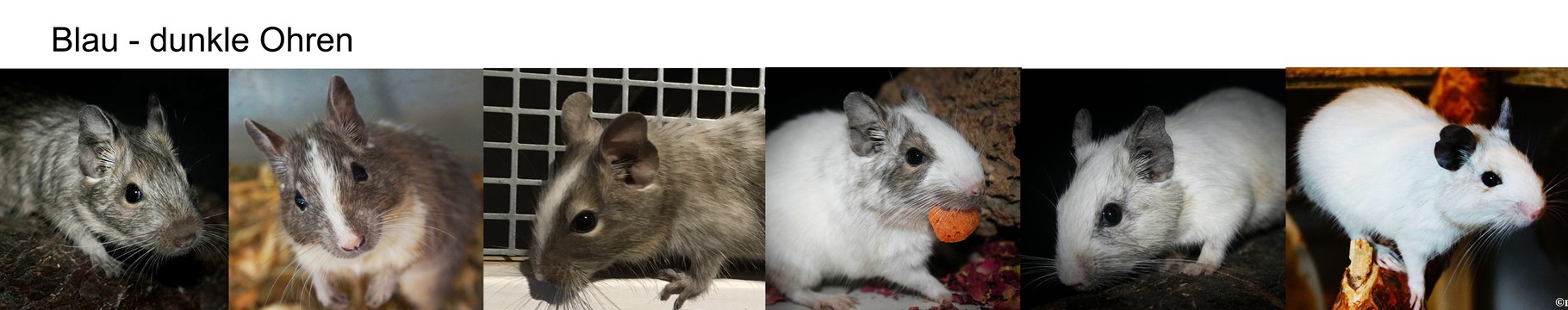
Blue PIEBALDS
Sand PIEBALDS
Cream PIEBALDS
Coming Soon
Black / Chocolate / BNA / Lilac
COLOR COMPARISONS


All texts and contents are subject to copyright, © dein-degu.de